When should you refer the patient to a doctor?
The benefits of taking Lovima should be weighed against the possible risks for women who have certain medical conditions, as listed below. Discuss these medical conditions with the woman before she decides to start taking Lovima. In the event of aggravation, exacerbation or first appearance of any of these condition, the woman should contact her doctor.
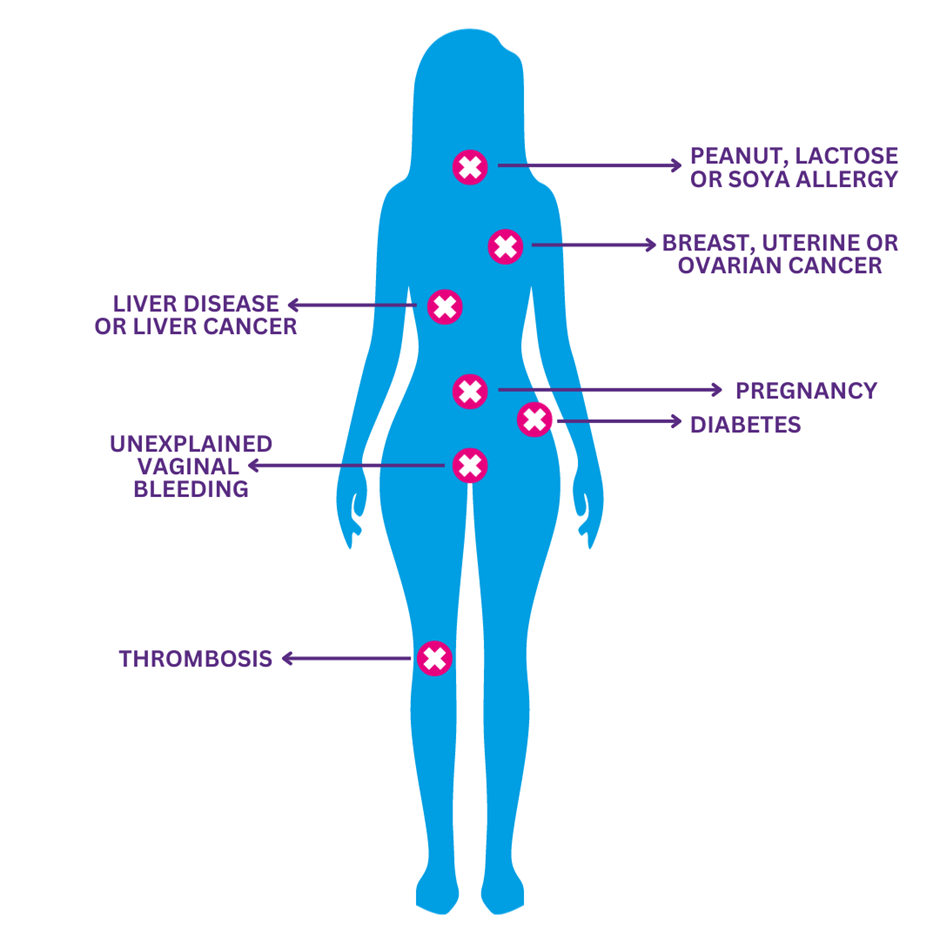
Fig 3 l Medical Conditions with possible risks when taking Lovima
Women with multiple co-morbidities should be referred to a doctor to assess the most suitable method of contraception for them.
| Condition | Context | Action |
| History of breast, uterine or ovarian cancer | As noted in the previous section, Lovima is contraindicated in patients who have known or suspected sex-steroid-sensitive malignancies, such as breast, uterine or ovarian cancer. Patients with a history of breast cancer require additional counselling on contraceptive options before starting Lovima because the risk of desogestrel is likely to outweigh the benefits. See 'breast cancer risk' section for further information. | Do not supply Lovima to patients with a history of breast, uterine or ovarian cancer. Refer her to her doctor. |
| Liver disease and liver cancer | As noted in the previous section, liver disease or history of liver disease (where liver function has not returned to normal) are contraindications to use of Lovima. As the metabolism of steroid hormones can be impaired in those with severe liver disease, use in these patients is contra-indicated. This includes liver cancer. A biological effect of progestogens on liver cancer cannot be excluded, and therefore an individual benefit/risk assessment should be made in women with liver cancer. As such, patients who have or have had liver cancer or liver disease should be advised to discuss contraceptive options with their doctor before starting Lovima. | Do not supply Lovima to patients with liver cancer or current or a previous history of liver disease. Refer her to her doctor. |
| Diabetes | Diabetes is not a contraindication for Lovima. Although progestogens may have an effect on peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, there is no evidence for a need to alter the therapeutic regimen in patients with diabetes (Type 1 or Type 2) using POPs. However, patients with diabetes should be carefully observed during the first months of use. | Do not supply Lovima to patients with diabetes considering Lovima and refer them to their doctor. |
| A history of thrombosis | As noted in the previous section, only an active VTE is a contraindication for Lovima. Women with a history of VTE are not contraindicated for Lovima but should be made aware of the possibility of recurrence. They may wish to discuss alternative contraception with their doctor or a family planning nurse. | Lovima can be supplied but additional counselling is required for those with a history of VTE. See 'cardiovascular risk' section for further information. |
| Hypertension (high blood pressure) | Hypertension is not a contraindication for Lovima. Checking and monitoring blood pressure is not a requirement for supply. However, obtaining a baseline blood pressure reading might be considered good practice as part of general health surveillance. Women found to have hypertension at any time should be referred to their doctor to discuss their antihypertensive treatment options. However, several drugs used to treat hypertension can increase the clearance of contraceptive hormones, leading to increased risk of contraceptive failure. | See the 'drug interactions' section for further information and guidance on how to advise such patients. |
CONSIDERATIONS WITH HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES

Diabetes
Although some progestogens may have an effect on peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, there is no evidence for a need to alter the therapeutic regimen in patients with diabetes using POPs. However, patients with diabetes should be carefully observed during the first months of use. For this reason, it is recommended that women talk to their doctor or nurse before using Lovima if they have Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes.

Blood pressure
There is no requirement to check blood pressure before or during treatment with Lovima. Unlike some combined oral contraceptive (COC) pills, hypertension (high blood pressure) is not a contraindication for POPs. The available evidence does not support an association between POPs and an increase in blood pressure. However, several antihypertensive drugs can interact with contraceptive hormones (see drug interactions section).

Weight
Unlike for some types of emergency contraception, increased dosages for women who are overweight or obese are not recommended for Lovima or other POPs. The currently available evidence indicates that the efficacy of POPs is not influenced by body weight or body mass index. In addition, there is no evidence suggesting a relationship between the POP and weight gain, although it is a commonly reported side effect ( see 'Possible side effects').

Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is not a contraindication for Lovima. Lovima does not appear to influence the production or the quality (protein, lactose or fat concentrations) of breast milk. However, there have been infrequent reports of a decrease in breast milk production while using desogestrel. A small amount of etonogestrel is excreted in the breast milk and may be ingested by the child.
Based on the available data, desogestrel may be used during lactation. The development and growth of a nursing infant whose mother uses desogestrel should however, be carefully monitored. This monitoring is expected to occur automatically through routine child health surveillance checks that are already in place in the UK for all children.

Migraines
Although data are limited, the currently available evidence does not suggest an increased risk of migraine with the use of POPs. There is no contraindication, warning or precaution required relating to use of Lovima in patients who suffer from migraines. This is contrast to COCs - the Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare (FSRH) recommends that use of COCs is either strongly cautioned or avoided for women who have migraines with aura or new-onset migraine without aura.
